CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
Carpal Tunnel as the name suggests, is a tunnel formed by carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. Through this tunnel courses a bundle of nerves, blood vessels and tendons that supply our hands.
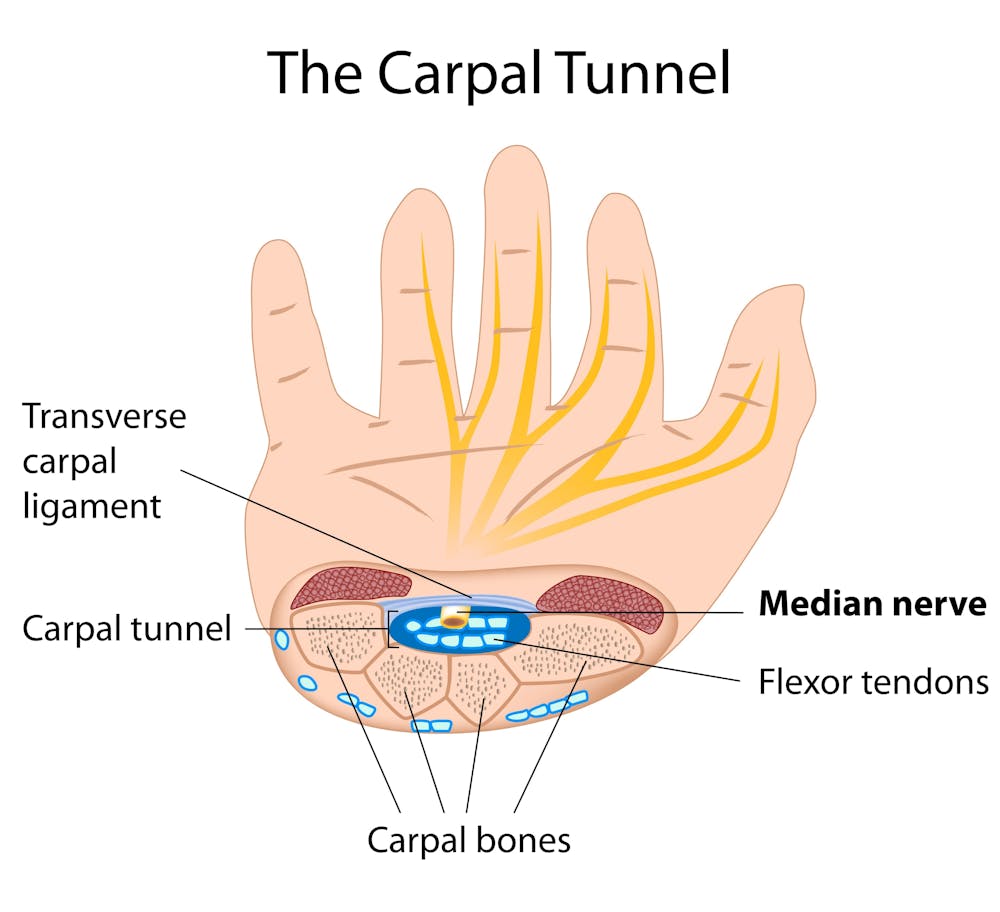
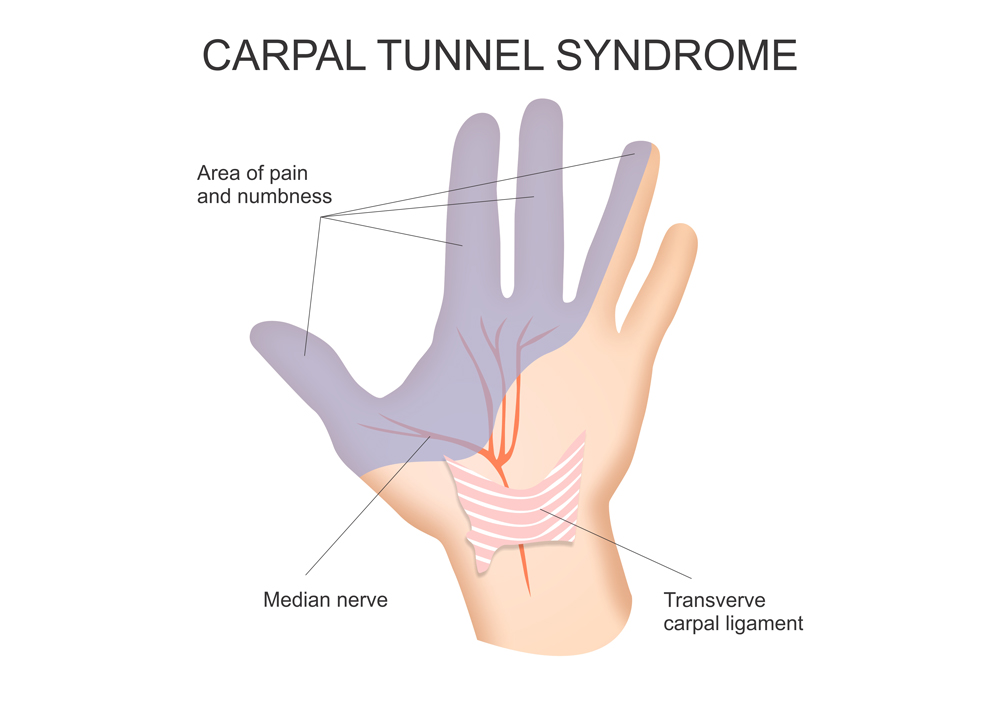
Median nerve passes through this tunnel. Sometimes tendons in the wrist become swollen which can result in the compression of the median nerve. This condition is often called Carpal tunnel syndrome.
Before we delve into the symptoms and treatments of carpal tunnel syndrome, we will first understand the areas supplied by the median nerve in our hand.
Median nerve generally supplies the LOAF muscles. These muscles are:
- Lumbricles
- Opponens Pollicis
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
Actions of the muscles supplied by the median nerve:
1. Lumbricles- Flexion of MCP joint and extension of IP joint
2. Opponens Pollicis- Opposition
3. Abductor Pollicis Brevis- Abduction of thumb
4. Flexor Pollicis Brevis- Flexes MCP joint of the thumb
Carpal tunnel syndrome results in pain, numbness and tingling sensation in the areas supplied by the median nerve in our hand.
This syndrome consists of motor, sensory, vasomotor and trophic symptoms in the hand.
- Motor changes- Loss of opposition of thumb.
- Sensory changes- Sensation loss on lateral side of the fingers.
- Vasomotor changes- Cutaneous area with loss of sensation is warmer due to arteriolar dilatation.
- Trophic changes- Dry and scaly skin.
Tests and diagnosis for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
1. Tinel's sign: .
The therapist taps or press the median nerve with a reflex hammer. If the patient feels pain or tingling sensation then it can be an indicative of carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Phalen's test:
It is also called wrist flexion test. The therapist flexes patient's wrist manually and holds together for one minute. If there is any pain or tingling sensation in the thumb, index finger and lateral half of the ring finger then it can be an indicative of carpal tunnel syndrome.

Treatment:
Splints:
Wearing a resting splint can help prevent
the symptoms occurring at night, or
a working splint can be useful if your
symptoms are brought on by particular
activities. Your doctor or physiotherapist
can advise on where you can be fitted
with a splint.
Steroid injections :
To reduce inflammation, your doctor or a
specialist physiotherapist can give you a
steroid injection into your carpal tunnel.
The injection may be uncomfortable, but
the effects can last for weeks or months.
A steroid injection into the wrist joint itself
may help if you have arthritis in your wrist.
Your pain should ease within
2 weeks and you should recover over
approximately a 4–6 week period.
You should use the exercises overleaf
for at least 6–8 weeks to help prevent
symptoms returning.
Exercises for Carpal tunnel syndrome:

Surgical treatments:
If the symptoms continue to appear then patient can undergo surgery.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete